

The first stage of interphase is called the G 1 phase, or first gap, because little change is visible.
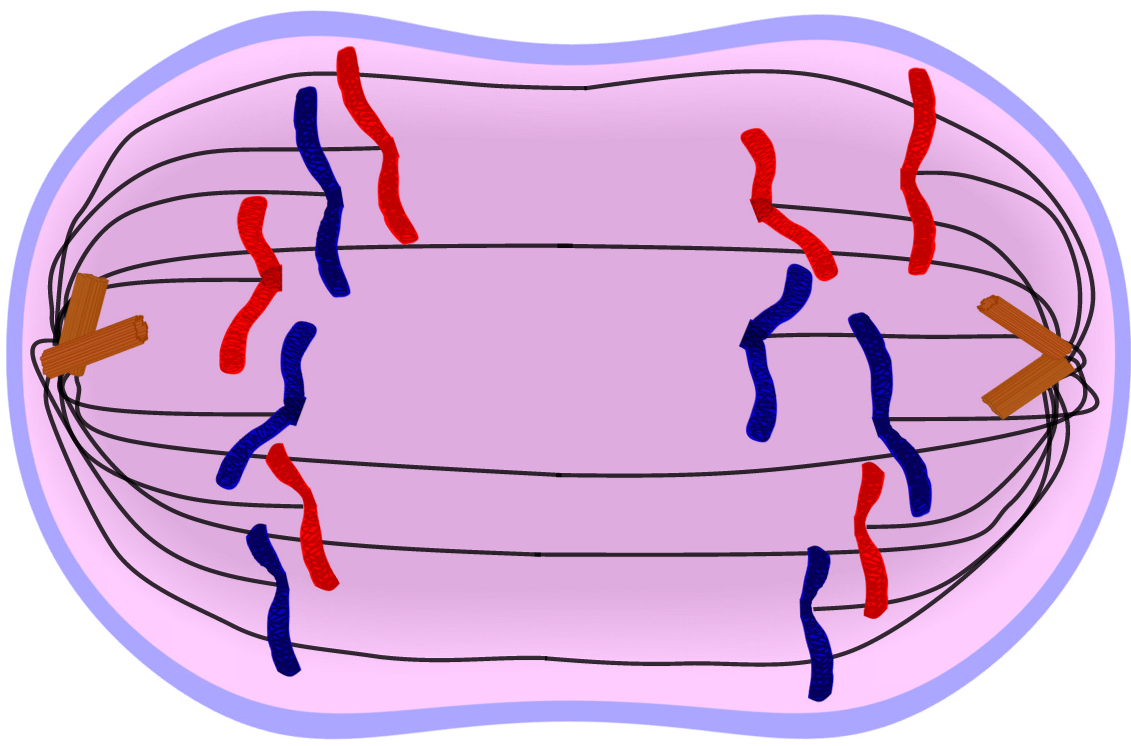

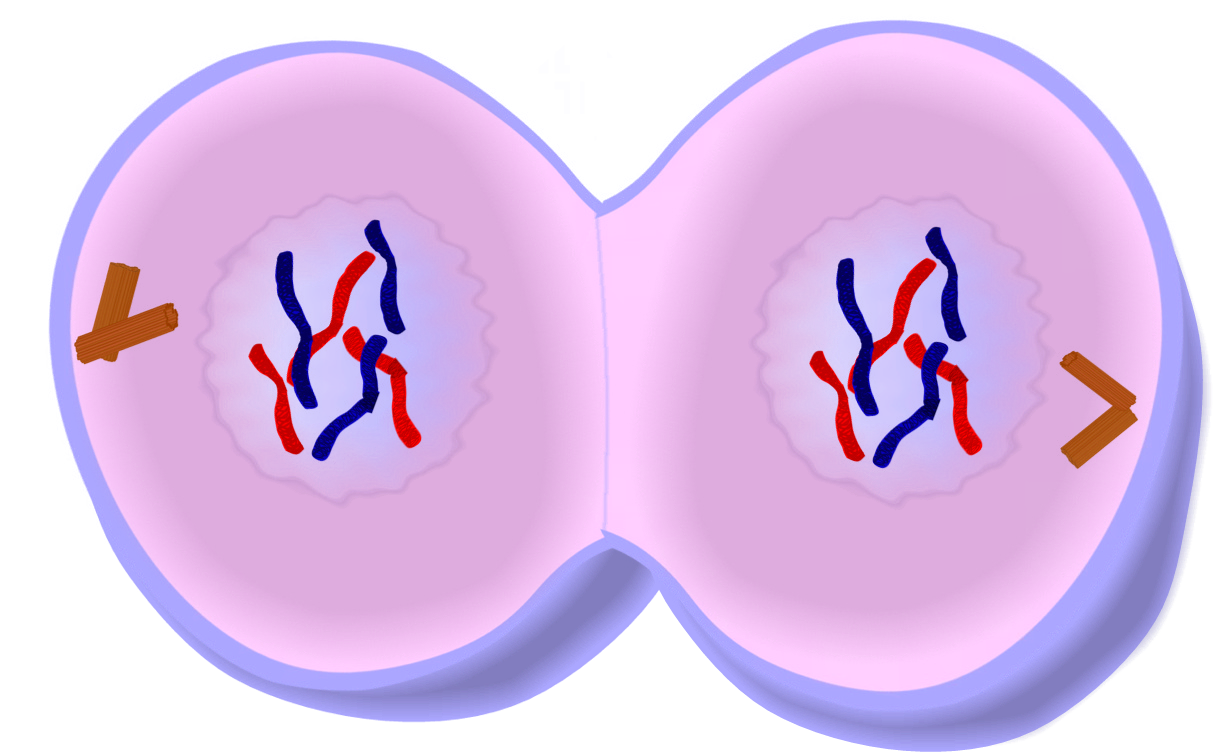
The three stages of interphase are called G 1, S, and G 2. For a cell to move from interphase to the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. Interphaseĭuring interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. Usually the cell will divide after mitosis in a process called cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm is divided and two daughter cells are formed. Mitosis is nuclear division during which duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. During interphase, G1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the S phase involves DNA replication and the replication of the centrosome, and G2 involves further growth and protein synthesis.
#PROPHASE 2 DEFINITION SERIES#
Watch this video about the cell cycle: Figure 6.3 A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. During the mitotic phase, the replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase ( Figure 6.3). Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of G 1, at the G 2–M transition, and during metaphase.Discuss the behavior of chromosomes during mitosis and how the cytoplasmic content divides during cytokinesis.Describe the three stages of interphase.Homologous chromosomes can exchange parts in a process called "crossing over.By the end of this section, you will be able to: In Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up. This shuffling process is known as recombination or "crossing over" and occurs while the chromome pairs are lined up in Metaphase I. Each sibling is 50% mom and 50% dad, but which 50% of each can vary in the siblings. But this happens independently for each trait, so just because you got your dad's brown eyes doesn't mean you'll get his blond hair too. Each sperm and egg will end up with either B or b from mom and either B or b from dad. This leads to four possibilities: You could get B from mom and B from dad, or B from mom and b from dad, or b from mom and B from dad, or b from mom and b from dad. Imagine, for example, that eye color was controlled by a single gene, and that mom could have B, the allele for brown eyes or b, the allele for blue eyes, and dad could also have B or b. But each non-identical-twin child of these parents ends up with a different combination. You ended up with half of mom's paired genes and half of dad's paired genes. Your parents each have at least one pair of alleles (versions of a gene) for every trait (and many pairs of alleles for each polygenic trait).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
